The elaboration processes of Cu/C composites based on powder metallurgy technology require the starting copper powder, typically from 10 and 30 pm, and short carbon fibres, typically from 1 to 10 mm of length. In opposite, the squeeze casting process does not require the short carbon fibres or copper powders, but continuous carbon fibres can be used in this route process.
The characteristics of copper powder and short carbon fibres have strong impact on the final structure and properties of composites. These characteristics can be listed as following points:
– Ratio size between copper particles and diameter of carbon fibres. High ratio is favourable to better distributions of carbon fibres in copper matrix, and a ratio higher that one is usually recommended.
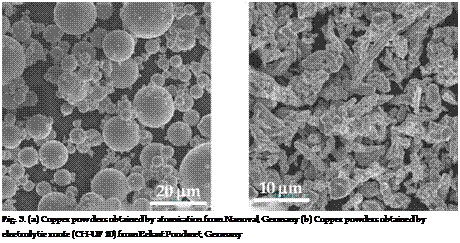
– The electrolytic copper powders (dendritic shape) lead to better mixing with short carbon fibres that copper powders obtained by atomisation (spherical shape).
– The length of carbon fibres must be 100 times greater than their diameter in order to obtain the optimal thermo-mechanical properties.
The following figures (fig. 3) show two main types of copper powder, the spherical copper particles obtained by atomisation and dendrite copper particles obtained by electrolytic route.
 ШЯ m ♦ і ■■ LkjUfcai
ШЯ m ♦ і ■■ LkjUfcai
(a) (b)
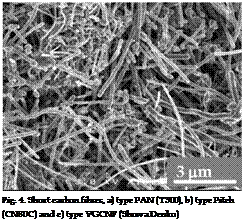
Two main types of carbon fibres are usually used for industrial applications: polyacrylonitrile (PAN) and Pitch. Most of the carbon fibres currently produced in the world is based on PAN. Pitch fibres are produced using existing hydrocarbon resources (petroleum and/or coal) as the raw material to derive high performance carbon materials and product with a textile manufacturing approach.
In comparison to PAN, pitch carbon fibres have higher modulus capability, (equivalent) negative CTE, and higher thermal and electrical conductivity. These properties come from higher crystallisation of carbon fibre after graphitization step at high temperature. However, the Pitch carbon fibres are often more expensive that the PAN carbon fibres. Then, the Pitch carbon fibres are more appropriated for the thermal management applications.
Recently, Vapor Growth Carbon Nano Fibres (VGCNF) have been developed for potential thermal applications with theorical thermal conductivity close to one of the diamond (1200 W/m. K). The VGCNF can be considered as an intermediate structure between carbon nanotubes and vapor growth carbon fibres. However, the properties of VGCNF have still been some controversy, since the strategy to measure their mechanical properties relies on non-conventional measurement techniques or inverse calculations from models.
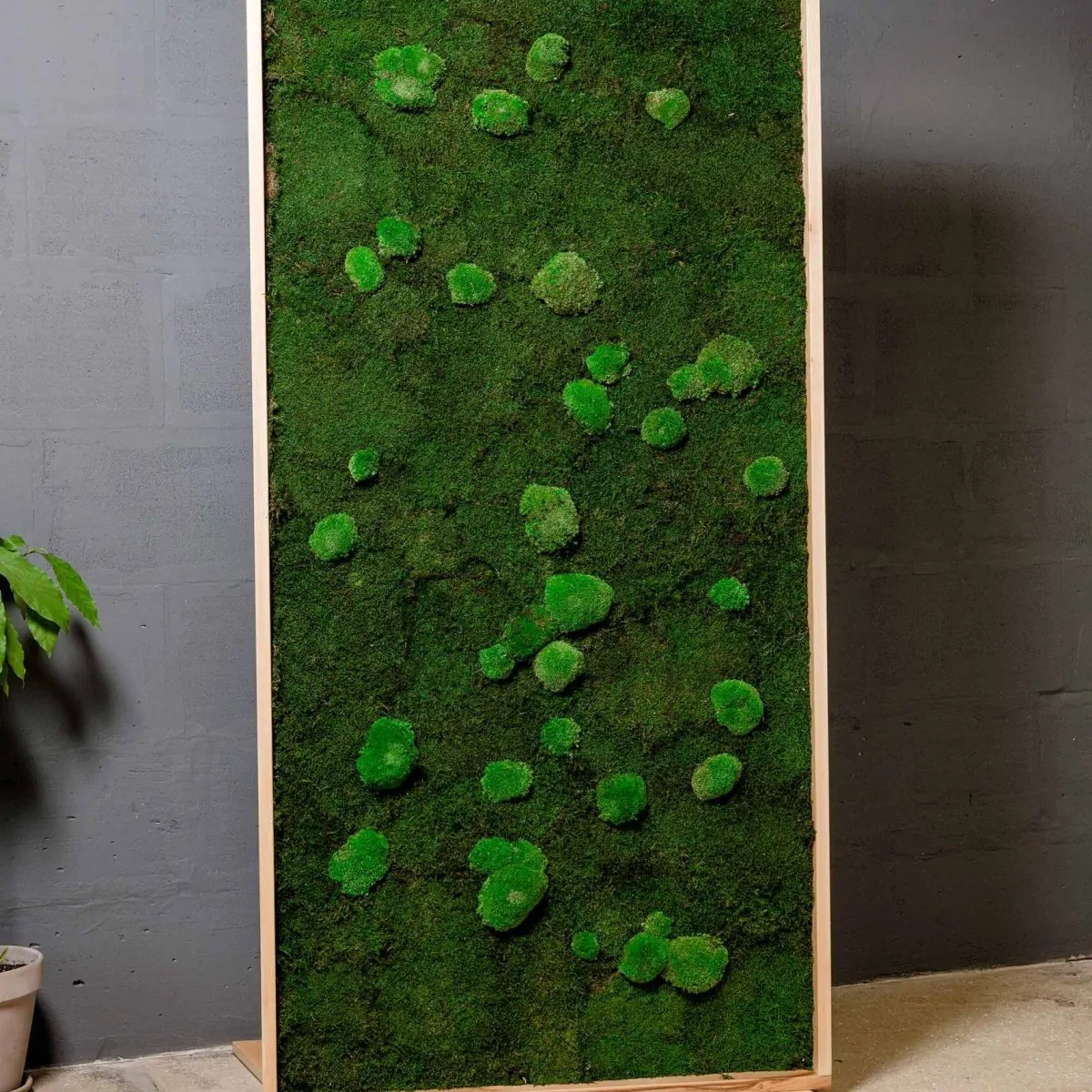
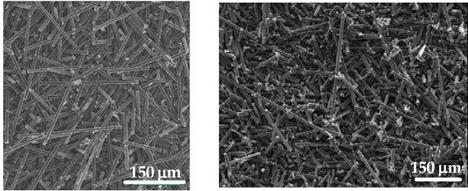
The copper particles have dendrite shape with a range size from 25 to 30 pm (Fig. 3b). Starting chopped carbon fibres have diameter ranging from 9 to 10 pm and mean length of 6
mm. After milling, using planetary mill in alumina jar and alumina balls, the mean length of carbon fibres is decreasing down to 100 to 200 pm (Fig. a, b and c). In fact, for carbon fibre length greater than 200 microns, the flowability of slurry decreases strongly leading to the impossibility of slurry casted thin film.
|
|
(a) (b)
(c)
The main physical characteristics of powders are given in Table 2.