As we are accustomed to look to Greek Art of the time of Pericles for purity of style and perfection of taste, so do we naturally expect the gradual demoralisation of art in its transfer to the great Roman Empire. From that little village on the Palatine Hill, founded some 750 years B. C., Rome had spread and conquered in every direction, until in the time of Augustus she was mistress of the whole civilised world, herself the centre of wealth, civilisation, luxury, and power. Antioch in the East and Alexandria in the South ranked next to her as great cities of the world.
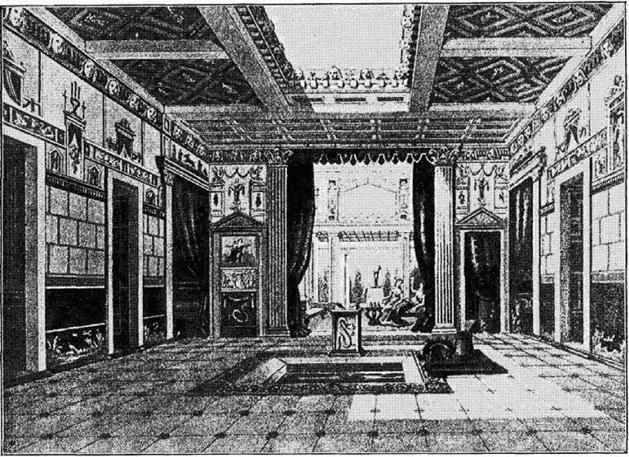
From the excavations of Herculaneum and Pompeii we have learned enough to conceive some general idea of the social life of a wealthy Roman in the time of Rome’s prosperity. The houses had no upper story, but were formed by the enclosure of two or more quadrangles, each surrounded by courts opening into rooms, and receiving air and ventilation from the centre open square or court. The illustration will give an idea of this arrangement.
In Mr. Hungerford Pollen’s useful handbook there is a description of each room in a Roman house, with its proper Latin title and purpose; and we know from other descriptions of Ancient Rome that the residences in the Imperial City were divided into two distinct classes—that of domus and insula, the former being the dwellings of the Roman nobles, and corresponding to the modern Palazzi, while the latter were the habitations of the middle and lower classes. Each insula consisted of several sets of apartments, generally let out to different families, and was frequently surrounded by shops. The houses described by Mr. Pollen appear to have had no upper story, but as ground became more valuable in Rome, houses were built to such a height as to be a source of danger, and in the time of Augustus there were not only strict regulations as to building, but the height was limited to 70 feet. The Roman furniture of the time was of the most costly kind.
|
INTERIOR OF AN ANCIENT ROMAN HOUSE. Said to have been that of Sallust. Period : b. c. 20 to a. d. 20. |
Tables were made of marble, gold, silver, and bronze, and were engraved, damascened, plated, and enriched with precious stones. The chief woods used were cedar, pine, elm, olive, ash, ilex, beech, and maple. Ivory was much used, and not only were the arms and legs of couches and chairs carved to represent the limbs of
 |
 |
animals, as has been noted in the Assyrian, Egyptian, and Greek designs, but other parts of furniture were ornamented by carvings in bas relief of subjects taken from Greek mythology and legend. Veneers were cut and applied, not as some have supposed for the purpose of economy, but because by this means the most beautifully marked or figured specimens of the woods could be chosen, and a much richer and more decorative effect produced than would be possible when only solid timber was used. As a prominent instance of the extent to which the Romans carried the costliness of some special pieces of furniture, we have it recorded on good authority (Mr. Pollen) that the table made for Cicero cost a million sesterces, a sum equal to about £9,000, and that one belonging to King Juba was sold by auction for the equivalent of £10,000.
Cicero’s table was made of a wood called Thyine—wood which was brought from Africa and held in the highest esteem. It was valued not only on account of its beauty but also from superstitious or religious reasons. The possession of thyine wood was supposed to bring good luck, and its sacredness arose from the fact that from it was produced the incense used by the priests. Dr. Edward Clapton, of St. Thomas’ Hospital, who has made a collection of woods named in the Scriptures, has managed to secure a specimen of thyine, which a friend of his obtained on the Atlas Mountains. It resembles the woods which we know as tuyere and amboyna.2
Roman, like Greek houses, were divided into two portions—the front for reception of guests and the duties of society, with the back for household purposes, and the
occupation of the wife and family; for although the position of the Roman wife was superior to that of her Greek contemporary, which was little better than that of a slave, still it was very different to its later development.
 |
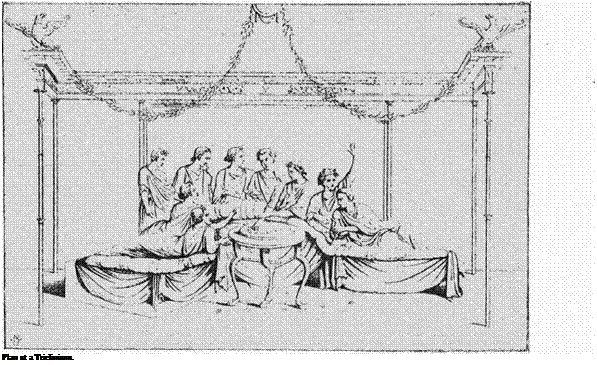
 |
The illustration given here of a repast in the house of Sallust, represents the host and his eight male guests reclining on the seats of the period, each of which held three persons, and was called a triclinium, making up the favorite number of a Roman dinner party, and possibly giving us the proverbial saying—"Not less than the Graces nor more than the Muses"—which is still held to be a popular regulation for a dinner party.
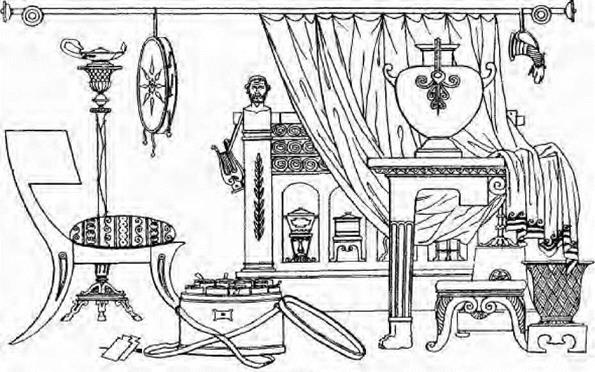
From discoveries at Herculaneum and Pompeii a great deal of information has been gained of the domestic life of the wealthier Roman citizens, and there is a useful illustration at the end of this chapter of the furniture of a library or study in which the designs are very similar to the Greek ones we have noticed; it is not improbable they were made and executed by Greek workmen.
It will be seen that the books such as were then used, instead of being placed on shelves or in a bookcase, were kept in round boxes called Sorinia, which were generally of beech wood, and could be locked or sealed when required. The books in rolls or sewn together were thus easily carried about by the owner on his journeys.
Mr. Hungerford Pollen mentions that wearing apparel was kept in vestiaria, or wardrobe rooms, and he quotes Plutarch’s anecdote of the purple cloaks of Lucullus, which were so numerous that they must have been stored in capacious hanging closets rather than in chests.
In the atrium, or public reception room, was probably the best furniture in the house. According to Moule’s "Essay on Roman Villas," "it was here that numbers assembled daily to pay their respects to their patron, to consult the legislator, to attract the notice of the statesman, or to derive importance in the eyes of the public from an apparent intimacy with a man in power."
The growth of the Roman Empire eastward, the colonisation of Oriental countries, and subsequently the establishment of an Eastern Empire, produced gradually an alteration in Greek design, and though, if we were discussing the merits of design and the canons of taste, this might be considered a decline, still its influence on furniture was doubtless to produce more ease and luxury, more warmth and comfort, than would be possible if the outline of every article of useful furniture were decided by a rigid adherence to classical principles. We have seen that this was more consonant with the public life of an Athenian; but the Romans, in the later period of the Empire, with their wealth, their extravagance, their slaves, their immorality and gross sensuality, lived in a splendour and with a prodigality that well accorded with the gorgeous colouring of Eastern hangings and embroideries, of rich carpets and comfortable cushions, of the lavish use of gold and silver, and meritricious and redundant ornament.
|
|
This slight sketch, brief and inadequate as it is, of a history of furniture from the earliest time of which we have any record, until from the extraordinary growth of the vast Roman Empire, the arts and manufactures of every country became as it were centralised and focussed in the palaces of the wealthy Romans, brings us down to the commencement of what has been deservedly called "the greatest event in history"—the decline and fall of this enormous empire. For fifteen generations, for some five hundred years, did this decay, this vast revolution, proceed to its conclusion. Barbarian hosts settled down in provinces they had overrun and conquered, the old Pagan world died as it were, and the new Christian era dawned. From the latter end of the second century until the last of the Western Caesars, in A. D. 476, it is, with the exception of a short interval when the strong hand of the great Theodosius stayed the avalanche of Rome’s invaders, one long story of the defeat and humiliation of the citizens of the greatest power the world has ever known. It is a vast drama that the genius and patience of a Gibbon has alone been able to deal with, defying almost by its gigantic catastrophes and ever raging turbulence the pen of history to chronicle and arrange. When the curtain rises on a new order of things, the age of Paganism has passed away, and the period of the Middle Ages will have commenced.
 |
А Каидм Нтігі’У.
 |
SheHins Strolh or Boobs tn a" Scirtnium ;n‘ ілтпр. Writing ТяЫг£н, etc