We have seen that Spain as well as Germany and the Low Countries were under the rule of the Emperor Charles V., and therefore it is unnecessary to look further for the sources of influence which brought the wave of Renaissance to the Spanish carvers and cabinet makers.
|
|
After Van Eyck was sent for to paint the portrait of King John’s daughter, the Low Countries continued to export to the Peninsula painters, sculptors, tapestry weavers, and books on Art. French artists also found employment in Spain, and the older Gothic became superseded as in other countries. Berruguete, a Spaniard, who had studied in the atelier of Michael Angelo, returned to his own country with the new influence strong upon him, and the vast wealth and resources of Spain at this period of her history enabled her nobles to indulge their taste in cabinets richly ornamented with repousse plaques of silver, and later of tortoiseshell, of ebony, and of scarce woods from her Indian possessions; though in a more general way chesnut was still a favorite medium.
Contemporary with decorative woodwork of Moorish design there was also a great deal of carving, and of furniture made, after designs brought from Italy and the North of Europe; and Mr. J. H. Pollen, quoting a trustworthy Spanish writer, Senor J. F. Riario, says:—"The brilliant epoch of sculpture (in wood) belongs to the sixteenth century, and was due to the great impulse it received from the works of Berruguete and Felipe de Borgona. He was the chief promoter of the Italian style, and the choir of the Cathedral of Toledo, where he worked so much, is the finest specimen of the kind in Spain. Toledo, Seville, and Valladolid were at the time great productive and artistic centres."
|
SuLvirt Тліні.. L*ie сСїи OB F.,imv 1 vrn СвктииY itII l/lf (/|1<Yrt’g CoUfttiun. 0 iturtllt Ca>Mr.) |
 The same writer, after discussing the characteristic Spanish cabinets, decorated outside with fine ironwork and inside with columns of bone painted and gilt, which were called "Varguenos," says:—"The other cabinets or escritoires belonging to that period (sixteenth century) were to a large extent imported from Germany and Italy, while others were made in Spain in imitation of these, and as the copies were very similar it is difficult to classify them." * * *
The same writer, after discussing the characteristic Spanish cabinets, decorated outside with fine ironwork and inside with columns of bone painted and gilt, which were called "Varguenos," says:—"The other cabinets or escritoires belonging to that period (sixteenth century) were to a large extent imported from Germany and Italy, while others were made in Spain in imitation of these, and as the copies were very similar it is difficult to classify them." * * *
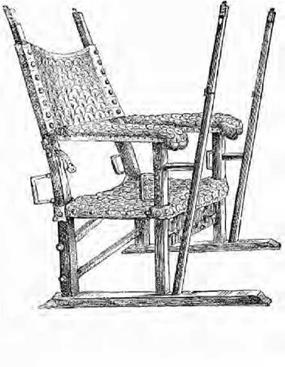
CHAIR OF WALNUT OR CMESNU T WOOD.
Cnvuml in I «-nlhtrr with emU.-M-d paiiern. Spanish ((.‘ullwcflor. Harou tie Valiisre >
I’bkiqd. Early Л. Л – li LT. WTt in
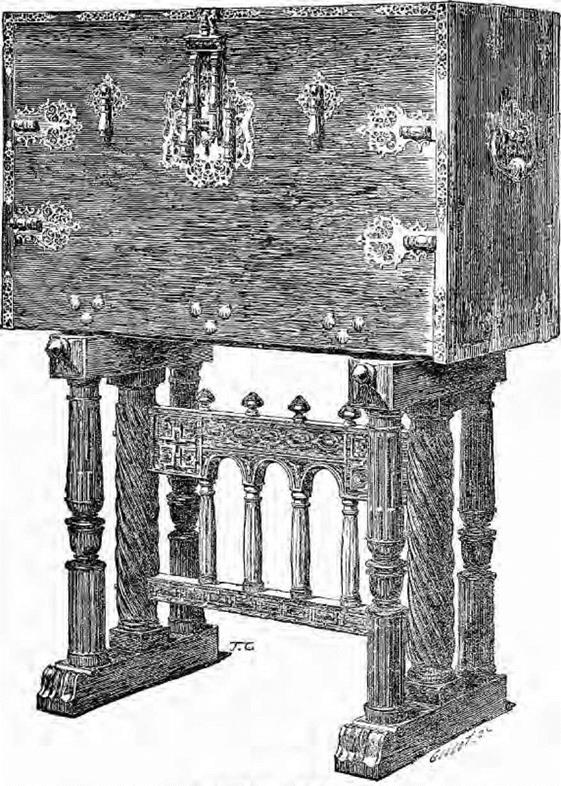 |
WOODEN COFFER.
Wiu: V/rfrtiifht ‘in’ inniiDtTi nijfl laJlftig flap, 11Ц c.–.rvc-1 – lOrnd, Spntiish
fCa’He-‘hon oi M Munbrison.)
PjftnfqSJ XVIT, СC-;Pftltrv
"Besides these inlaid cabinets, others must have been made in the sixteenth century inlaid with silver. An Edict was issued in 1594, prohibiting, with the utmost rigour, the making and selling of this kind of merchandise, in order not to increase the scarcity of silver." The Edict says that "no cabinets, desks, coffers, braziers, shoes, tables, or other articles decorated with stamped, raised, carved, or plain silver should be manufactured."
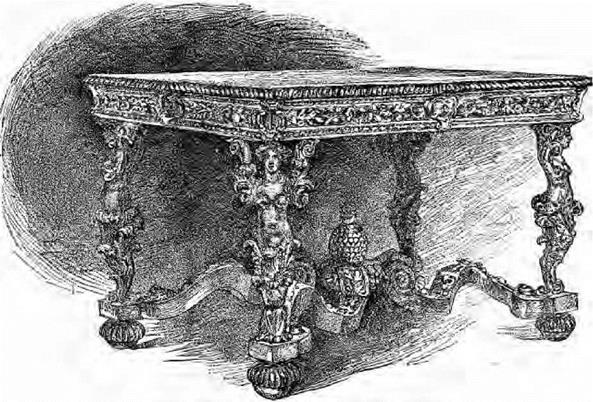
The beautiful silver table in Her Majesty’s collection at Windsor Castle, illustrated on page 68, is probably one of Spanish make of late sixteenth or early seventeenth century.
Although not strictly within the period treated of in this chapter, it is convenient to observe that much later, in the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries, one finds the Spanish cabinet maker ornamenting his productions with an inlay of ivory let into tortoiseshell, representing episodes in the history of Don Quichotte, and the National pastime of bull-fighting. These cabinets generally have simple rectangular outlines with numerous drawers, the fronts of which are decorated in the manner described, and where the stands are original they are formed of turned legs of ebony or stained wood. In many Spanish cabinets the influence of Saracenic art is very dominant; these have generally a plain exterior, the front is hinged as a fall – down flap, and discloses a decorative effect which reminds one of some of the Alhambra work—quaint arches inlaid with ivory, of a somewhat bizarre coloring of blue and vermilion—altogether a rather barbarous but rich and effective treatment.
To the seventeenth century also belong the high-backed Spanish and Portuguese chairs, of dark brown leather, stamped with numerous figures, birds and floral scrolls, studded with brass nails and ornaments, while the legs and arms are alone visible as woodwork; they are made of chesnut, with some leafwork or scroll carving. There is a good representative woodcut of one of these chairs.
Until Baron Davillier wrote his work on Spanish art, very little was known of the different peculiarities by which we can now distinguish examples of woodwork and furniture of that country from many Italian or Flemish contemporary productions. Some of the Museum specimens will assist the reader to mark some characteristics, and it may be observed generally that in the treatment of figure subjects in the carved work, the attitudes are somewhat strained, and, as has been stated, the outlines of the cabinets are without any special feature. Besides the Spanish chesnut (noyer), which is singularly lustrous and was much used, one also finds cedar, cypress wood and pine.
In the Chapel of Saint Bruno, attached to the Carthusian Convent at Granada, the doors and interior fittings are excellent examples of inlaid Spanish work of the seventeenth century; the monks of this order at a somewhat earlier date are said to have produced the "tarsia," or inlaid work, to which some allusion has already been made.