1.3.1 Shearing buckling of thin plates
In this chapter, the thickness and the lay-up of the plate are according to Table AA1. The plate, considered as clamped on the sides, was loaded with an uniform shear pressure on the sides (Fig. AA14). The force was increased step by step (with and certain increment).
|
|
Fig. 17.14. Shear loaded plate with central delamination
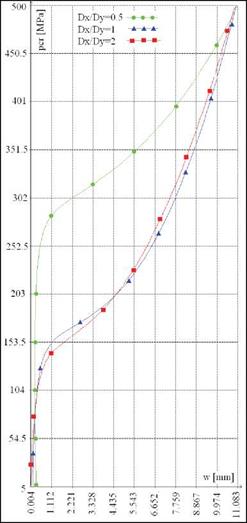
In the figure AA15, the variation of the transversal displacements of the central point, versus applied loading is drawn, for delamination placed between macro-layers 4 and 5. Each curve corresponds to one diameters ratio.
|
Fig. 17.15. Shear buckling and post buckling behaviour of the plates with central delamination placed between macro-layers 4 and 5 |
Buckling load has been determined by the graphical method (an asymptote on curve after the bifurcation has been plotted).
Critical value for the buckling load was obtained in the range 109 MPa < pcr <289 MPa.
In the case of nonlinear model of the material behaviour the buckling load (ultimate strength) was determined by Tsai Wu criterion. So, the degradation index (failure index) for
tension and compression of the delaminated plates was determined (Table AA6). Only the plate global buckling was examined.
|
Dx/Dy |
0.5 |
1 |
2 |
|
|
Position of delamination |
Fail type |
|||
|
Macro-layer 1 |
Traction |
25 |
20 |
20 |
|
Macro-layer 2 |
Compression |
90 |
– |
– |
|
Macro-layer 2 |
Traction |
25 |
20 |
20 |
|
Macro-layer 3 |
Compression |
90 |
– |
– |
|
Macro-layer 3 |
Traction |
25 |
20 |
20 |
|
Macro-layer 4 |
Compression |
90 |
– |
– |
|
Macro-layer 4 |
Traction |
25 |
20 |
20 |
|
Macro-layer 5 |
Compression |
90 |
– |
– |
|
Table 17.6. Buckling load (ultimate strength) in [MPa] for shear loading of the plates |