No career field in ornamental horticulture holds greater promise than interior plantscaping. The current technology and knowledge of growing plants indoors is comparable to that when Henry Ford and the Wright Brothers began working in their professions. There is a need for fresh approaches to move us beyond Ficus trees and hanging baskets. More research is needed to introduce new species and varieties suitable for interior use. Also needed is better data on how to acclimatize plants with less foliage drop and transplant shock. Further study of soil mixes, fertilizer needs, and lighting requirements is needed to replace the guesswork of today. Finally, more professional plant maintenance firms are needed. They need dependable studies of such matters as the time required to dust and clean various leaf sizes and textures. Buildings need to be designed as carefully for their planted occupants as for their human ones. Automated watering and fertilization systems are needed to ease the current labor-intensive methods. There is ample work for young people who wish to train themselves for it.
SUMMARY______________________________________
The use of plants indoors is not a new idea. Nevertheless, so explosive has been the recent demand for interior plantings in public buildings that the technology necessary to ensure their survival has not kept pace.
In general, tropical foliage plants have proved better suited than temperate zone plants for indoor use because they do not require a period of cool temperature dormancy. Nevertheless, when plants are used indoors, a number of problems can occur. The procedures necessary for the successful transplant of tropical foliage plants to an interior locale include acclimatization to reduced light intensity, reduced nutrients, greater moisture stress, and lower temperatures.
Although light acclimatization allows the plant to survive at a reduced light intensity, it is still vital that the proper quality of light be provided. Therefore, the designer of an interior plantscape must understand the differences in light quality and the lamps that provide them.
The provision of a proper growing medium is equally important to the successful acclimatization of interior plants. The medium must provide structural support, water absorption, essential nutrients, proper pH, and good drainage. It is most often a mixture of natural soil and additives.
Plants may be set into an interior plantscape in ground beds or raised planters. the method of installation will be determined partly by the anticipated frequency of plant replacement. Whether planting in ground or in planters, allowance must be made for the removal of standing water from the planters. More interior plantings die from overwatering than from any other reason.
Watering the plantings, like other procedures, needs to be done as part of a carefully planned program of maintenance. Scheduled maintenance, rather than impromptu attention, is necessary to ensure optimum satisfaction with the plantscape.
The most successful interior plantings require the expertise and cooperation of interior plantscapers, plant growers, interior decorators, landscape architects, architects, maintenance professionals, and building management. Each brings a distinct point of view to the project from which all others, and the plantscape, can benefit.
 |
 |
 |
ACHIEVEMENT REVIEW
C.
 |
 |
SHORT ANSWER
Answer each of the following questions as briefly as possible.
1. Place Xs in the chart below where appropriate to compare the different lamp types.
|
Characteristic |
Incandescent |
Cool White Fluorescent |
Fluorescent Plant Lamps |
Mercury |
Metal Halide |
High-Pressure Sodium |
|
High in red light |
||||||
|
Low in red light |
||||||
|
High in blue light |
||||||
|
Low in blue light |
||||||
|
Good color rendition |
||||||
|
High initial cost |
||||||
|
Low initial cost |
||||||
|
Moderate initial cost |
||||||
|
Low operating cost |
||||||
|
Moderate operating cost |
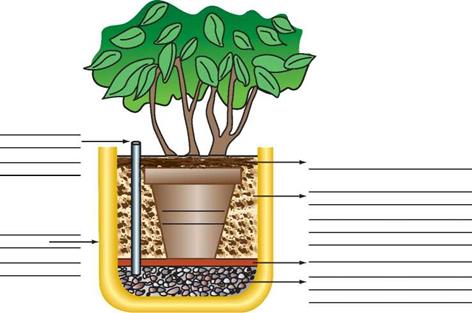
2. Label the parts of this containerized plant.
|
|
3. Indicate whether the following are characteristic of interior or exterior plantings
a. Rapid growth is encouraged
b. Pruning is minimal
c. Dusting of foliage is needed
d. High-analysis fertilizers are used regularly
e. Ventilation of the planting site is needed
f. Plants must be acclimatized to low humidity
g. Plants are most affected by insects and diseases
h. Plants suffer most from vandalism and abuse
![]()