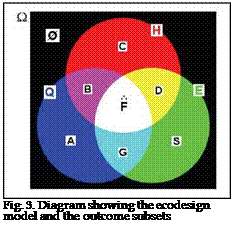
As it was shown in Figure 2c, the interaction between the three Q-H-E aspects yields the apparition of a certain number of events, which are illustrated in Figure 3. Each event is assumed to accomplish one or several functions that are defined by the following subsets (Attaf, 2007)
• Subset A (■): characterized by an assured quality, a non-protected health and a non-
preserved environment.
• Subset B (■): characterized by an assured quality, a protected health and a non-
preserved environment.
• Subset C (■): characterized by a non-assured quality, a protected health and a non-
preserved environment.
• Subset D (■): characterized by a non-assured quality, a protected health and a preserved
environment.
• Subset S (■): characterized by an assured quality, a non-protected health and a
preserved environment.
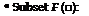 characterized by an assured quality, a protected health and a preserved environment.
characterized by an assured quality, a protected health and a preserved environment.
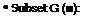
characterized by an assured quality, a non-protected health and a preserved environment.
The possible outcome sets and subsets can be expressed by the universal sample space as (Attaf, 2007)
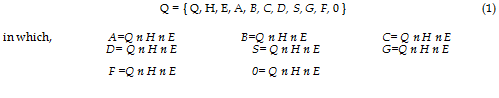 where, n denotes intersection symbol, and Q, H, E are the complement of Q, H, E and indicate that ”Quality non-realizable", "Health non-realizable" and "Environment nonrealizable", respectively.
where, n denotes intersection symbol, and Q, H, E are the complement of Q, H, E and indicate that ”Quality non-realizable", "Health non-realizable" and "Environment nonrealizable", respectively.
The subsequent analysis will concentrate only on the subset F, a unique searched subset that characterises the event: "intersection between Q, H and E does exist all the time".



