The transverse tensile strength is a main evaluating indicator for NASC in engineering, and its prediction may be performed according to 3 cases, as follows.
1. Debonding of interface from fiber
In this case, the transverse tensile strength can be calculated by
Eq. (35) can be used to predict the transverse tensile strength assuming that all fibers orientate in the same direction at the moment the matrix debonds from the fibers. If the fibers orientate in different directions, some will bear the longitudinal load. In this case, the transverse tensile strength is larger than that calculated by Eq. (35), and it can be calculated by Eq. (36).
2. Debonding of interface from matrix
 |
|||
If all fibers orientate in the same direction at the moment the interface debonds from the matrix, the transverse tensile strength can be calculated by Eq. (37).
If fibers orientate in different directions, стJH can be calculated by Eq. (38).
3. Damage of interface
The transverse tensile strength can be calculated by
Using Eq. (39), the transverse tensile strength can be predicted assuming that all fibers orientate in the same direction at the moment the interface is damaged. If fibers orientate in different directions, can be calculated by Eq. (40).
 |
|
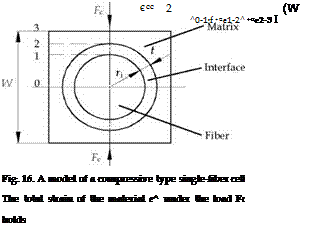
16) is established to derive the compression-creep constitutive equation of NASC with the assumption L~Z. The cell model is divided into three parts along compression-resilience direction; the first part consists of matrix, interface and fiber (0-1), the second part consists of matrix and interface (1-2), and the third part includes only matrix (2-3).
The compressive stress and strain of material relate to time. The compression-creep constitutive equation of NASC is in the form
The compression rate of NASC can be calculated by
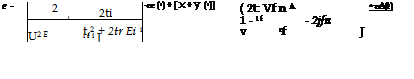 |
|
Substituting AT=0 into Eq. (43) gives the compressive rate of NASC at room temperature. The compressive strain can be calculated by
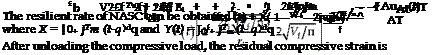 |
|
where
Substituting AT=0 into Eq. (46) gives the resilient rate of NASC at room temperature.



