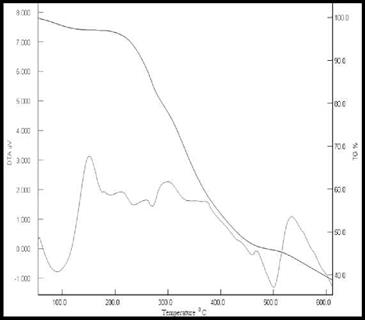
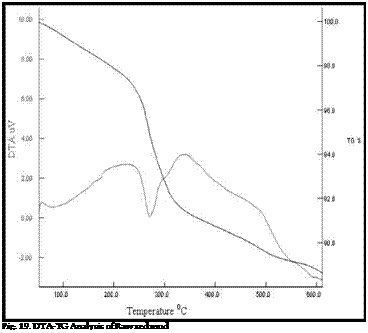
The thermal stability of the raw red mud, ORM, pure PVA and PVA nanocomposite membranes with different filler content was investigated by thermogravimetric analysis. The TGA thermograms of the raw red mud, ORM, and PVA – nanocomposite films are shown in Fig. 19, Fig.20 and Fig. 21 respectively. The raw red mud is thermally stable up to 267 oC while ORM is stable upto 243 oC. Although ORM has 37% residue at 600°C, raw red mud is more stable, with 88% residue at 600°C. Raw red mud suffers an 11% weight loss at 600°C because of the probable loss of volatile impurities.
|
|
|
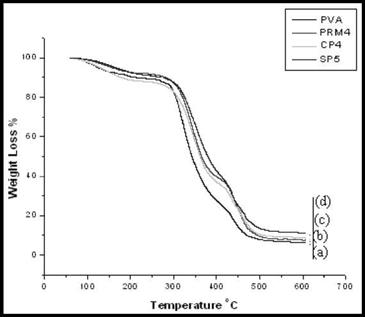
Fig. 21. Shows thermograms of (a) PVA (b) PRM4 (c) CP4 (d) SP5 film |
|
Sample |
Ti (o C) |
Tf (o C) |
Ash (%) |
|
Raw red mud |
267 |
356 |
88 |
|
ORM |
243 |
482 |
37 |
|
Pure PVA |
252 |
442 |
4.12 |
|
PRM4 |
274 |
462 |
7.23 |
|
CP4 |
277 |
467 |
10.13 |
|
SP5 |
281 |
474 |
12.43 |
|
Table 10. Degradation temperatures and ash content of the raw red mud, ORM, Pristine PVA and the PVA-nanocomposite membranes |
The pristine PVA is thermally stable up to 250 oC. The PVA nanocomposite membranes show enhanced thermal stability; the thermal degradation of the PVA nanocomposites generally showed two major weight loss steps. The first weight loss of 15-20 wt % is centered on 150 oC and corresponds to weight loss of absorbed water and structural water of the polymer nanocomposite membranes. The weight losses in the temperature ranges of 353-483°C can be attributed mainly to the subsequent structural decomposition of the polymer backbones at higher temperatures. Evidently, the thermal decomposition of the polymer nanocomposite materials shift slightly towards the higher temperature range than that of pure PVA, which confirms the enhancement of thermal stability of intercalated polymer [Lee & Jang, 1996]. The Polymer nanocomposite membrane with critical loading of SP5, showed better thermal stability as compared to CP4 and PRM4. This could be due to better intercalation of polymer matrix within the silicate galleries of SP5 while in case of
CP4, inspite of partial exfoliation and intercalation, thermal stability is considerably lesser than SP5 .This could be due to presence of organic moiety in CP4 which causes a decrease in its thermal stability. After, 500°C, the curve all became flat and mainly the inorganic residue (i. e. Al2O3, MgO, and SiO2) remained.