|
OBJECTIVES
Upon completion of this chapter, you should be able to
• describe the characteristics of sexual and asexual reproduction in plants.
• describe the processes of mitosis and meiosis.
• list the most common methods of propagating plants.
• recognize the contributions of Mendel to the science of genetics.
• discuss methods of plant improvement.
KEY TERMS
|
reproduction |
cytokinesis |
grafting |
|
propagation |
scarification |
budding |
|
plant propagators |
stratification |
tissue culture |
|
sexual reproduction |
clone |
apomictic embryos |
|
haploidal |
ramet |
chromosomes |
|
diploidal |
clonal varieties |
gene |
|
zygote |
runners |
gametes |
|
meiosis |
stolons |
phenotype |
|
homologous chromosomes |
sucker |
monohybrid cross |
|
homozygous |
bulbs |
dihybrid |
|
asexual reproduction |
layering |
hybrid vigor |
|
mitosis |
cuttings |
PLANT REPRODUCTION DEFINED___________________
When organisms duplicate themselves, the process is termed reproduction. Although only partially understood, plant reproduction is recognized as a complicated process that results in the multiplication of cells and the organisms that they make up. When reproduction is deliberately
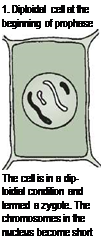
controlled and manipulated, it becomes propagation. Ornamental horticulturists who control the reproduction of plants are called plant propagators. In large operations, this can be a full-time occupation.



