European influence upon Indian art and manufactures has been of long duration; it was first exercised by the Portuguese and Dutch in the early days of the United East India Company, afterwards by the French, who established a trading company there in 1664, and since then by the English, the first charter of the old East India Company dating as far back as 1600. Thus European taste dominated almost everything of an ornamental character until it became difficult to find a decorative article the design of which did not in some way or other shew the predominance of European influence over native conception. Therefore it becomes important to ascertain what kind of furniture, limited as it was, existed in India during the period of the Mogul Empire, which lasted from 1505 to 1739, when the invasion of the Persians under Kouli Khan destroyed the power of the Moguls; the country formerly subject to them was then divided amongst sundry petty princes.
The thrones and State chairs used by the Moguls were rich with elaborate gilding; the legs or supports were sometimes of turned wood, with some of the members carved; the chair was formed like an hour glass, or rather like two bowls reversed, with the upper part extended to form a higher back to the seat. In M. Racinet’s sumptuous work, "Le Costume Historique," published in Paris in 20 volumes (1876), there are reproduced some old miniatures from the collection of M. Ambroise Didot. These represent—with all the advantages of the most highly finished printing in gold, silver, and colours—portraits of these native sovereigns seated on their State chairs, with the umbrella, as a sign of royalty. The panels and ornaments of the thrones are picked out with patterns of flowers, sometimes detached blossoms, sometimes the whole plant; the colors are generally bright red and green, while the ground of a panel or the back of a chair is in silver, with arabesque tracery, the rest of the chair being entirely gilt. The couches are rectangular, with four turned and carved supports, some eight or ten inches high, and also gilt. With the exception of small tables, which could be carried into the room by slaves, and used for the light refreshments customary to the country, there was no other furniture. The ladies of the harem are represented as being seated on sumptuous carpets, and the walls are highly decorated with gold and silver and color, which seems very well suited to the arched openings, carved and gilt doors, and brilliant costumes of the occupants of these Indian palaces.
After the break up of the Mogul power, the influence of Holland, France, and England brought about a mixture of taste and design which, with the concurrent alterations in manners and customs, gradually led to the production of what is now known as the "Bombay furniture." The patient, minute carving of Indian design applied to utterly uncongenial Portuguese or French shapes of chairs and sofas, or to the familiar round or oval table, carved almost beyond recognition, are instances of this style. One sees these occasionally in the house of an Anglo-Indian, who has employed native workmen to make some of this furniture for him, the European chairs and tables being given as models, while the details of the ornament have been left to native taste.
It is scarcely part of our subject to allude to the same kind of influence which has spoiled the quaint bizarre effect of native design and workmanship in silver, in jewellery, in carpets, embroideries, and in pottery, which was so manifest in the contributions sent to South Kensington at the Colonial Exhibition, 1886. There are in the Indian Museum at South Kensington several examples of this Bombay furniture, and also some of Cingalese manufacture.
In the Jones Collection at South Kensington Museum, there are two carved ivory chairs and a table, the latter gilded, the former partly gilded, which are a portion of a set taken from Tippo Sahib at the storming of Seringapatam. Warren Hastings brought them to England, and they were given to Queen Charlotte. After her death the set was divided; Lord Londesborough purchased part of it, and this portion is now on loan at the Bethnal Green Museum.
The Queen has also amongst her numerous Jubilee presents some very handsome ivory furniture of Indian workmanship, which may be seen at Windsor Castle. These, however, as well as the Jones Collection examples, though thoroughly
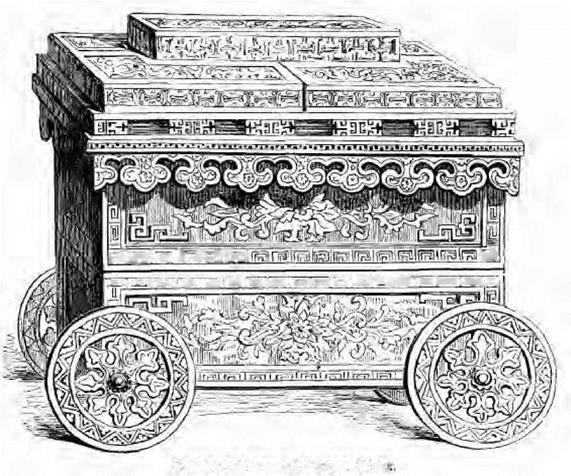
Indian in character as regards the treatment of scrolls, flowers, and foliage, shew unmistakcably the influence of French taste in their general form and contour. Articles, such as boxes, stands for gongs, etc., are to be found carved in sandal wood, and in dalburgia, or black wood, with rosewood mouldings; and a peculiar characteristic of this Indian decoration, sometimes applied to such small articles of furniture, is the coating of the surface of the wood with red lacquer, the plain parts taking a high polish while the carved enrichment remains dull. The effect of this is precisely that of the article being made of red sealing wax, and frequently the minute pattern of the carved ornament and its general treatment tend to give an idea of an impression made in the wax by an elaborately cut die. The casket illustrated on p. 134 is an example of this treatment. It was exhibited in 1851.
The larger examples of Indian carved woodwork are of teak; the finest and most characteristic specimens within the writer’s knowledge are the two folding doors which were sent as a present to the Indian Government, and are in the Indian Museum. They are of seventeenth century work, and are said to have enclosed a library at Kerowlee. While the door frames are of teak, with the outer frames carved with bands of foliage in high relief, the doors themselves are divided into panels of fantastic shapes, and yet so arranged that there is just sufficient regularity to please the eye. Some of these panels are carved and enriched with ivory flowers, others have a rosette of carved ivory in the centre, and pieces of talc with green and red colour underneath, a decoration also found in some Arabian work. It is almost impossible to convey by words an adequate description of these doors; they should be carefully examined as examples of genuine native design and workmanship. Mr. Pollen has concluded a somewhat detailed account of them by saying:—"For elegance of shape and proportion, and the propriety of the composition of the frame and sub-divisions of these doors, their mouldings and their panel carvings and ornaments, we can for the present name no other example so instructive. We are much reminded by this decoration of the pierced lattices at the S. Marco in Venice."
There is in the Indian Museum another remarkable specimen of native furniture— namely, a chair of the purest beaten gold of octagonal shape, and formed of two bowls reversed, decorated with acanthus and lotus in repousee ornament. This is of eighteenth century workmanship, and was formerly the property of Runjeet Sing. The precious metal is thinly laid on, according to the Eastern method, the wood underneath the gold taking all the weight.
There is also a collection of plaster casts of portions of temples and palaces from a very early period until the present time, several having been sent over as a loan to the Indian and Colonial Exhibition of 1886, and afterwards presented by the Commissioners to the Museum.
 lrj[lff3i і і ггіїПІГпІІ іі’ЬГІЇрЗї 1|іТЙ ч=ч |.: = ■ ■■ j іЧгіг’, lf-.ll I LEIJ і Ч^і~і 1Ы11 ^ ) L=U l|^fl^rri^Tibj]l^t^3|tSJil^*LDTl
lrj[lff3i і і ггіїПІГпІІ іі’ЬГІЇрЗї 1|іТЙ ч=ч |.: = ■ ■■ j іЧгіг’, lf-.ll I LEIJ і Ч^і~і 1Ы11 ^ ) L=U l|^fl^rri^Tibj]l^t^3|tSJil^*LDTl
Casket о и let шал Ьлс^чек Woki
A careful observation of the ornamental details of these casts leads us to the conclusion that the Byzantine style which was dominant throughout the more civilized portion of Asia during the power of the Romans, had survived the great changes of the Middle Ages. As native work became subject more or less to the influence of the Indo-Chinese carvers of deities on the one side, and of the European notions of the Portuguese pioneers of discovery on the other, a fashion of decorative woodwork was arrived at which can scarcely be dignified by the name of a style, and which it is difficult to describe. Dr. Birdwood, in his work on Indian Art, points out that, about a hundred years ago, Indian designs were affected by the immigration of Persian designers and workmen. The result of this influence is to be seen in the examples in the Museum, a short notice of which will conclude these remarks on Indian work.
The copy in shishem wood of a carved window at Amritzar, in the Punjaub, with its overhanging cornice, ornamental arches, supported by pillars, and the whole surface covered with small details of ornament, is a good example of the sixteenth and seventeenth century work. The various facades of dwelling-houses in teak wood, carved, and still bearing the remains of paint with which part of the carving
was picked out, represent the work of the contemporary carvers of Ahmedabad, famous for its woodwork.
Portions of a lacquer work screen, similar in appearance to embossed gilt leather, with the pattern in gold, on a ground of black or red, and the singular Cashmere work, called "mirror mosaic," give us a good idea of the Indian decoration of the eighteenth and early nineteenth centuries. This effective decoration is produced by little pieces of looking-glass being introduced into the small geometrical patterns of the panels; these, when joined together, form a very rich ceiling.
The bedstead of King Theebaw, brought from Mandalay, is an example of this mixture of glass and wood, which can be made extremely effective. The wood is carved and gilt to represent the gold setting of numerous precious stones, which are counterfeited by small pieces of looking-glass and variously-coloured pieces of transparent glass.
Some of the Prince of Wales’ presents, namely, chairs, with carved lions forming arms; tables of shishem wood, inlaid with ebony and ivory, shew the European influence we have alluded to.
Amongst the modern ornamental articles in the Museum are many boxes, pen trays, writing cases, and even photograph albums of wood and ivory mosaic work, the inlaid patterns being produced by placing together strips of tin wire, sandal wood, ebony, and of ivory, white, or stained green: these bound into a rod, either triangular or hexagonal, are cut into small sections, and then inlaid into the surface of the article to be decorated.
Papier mache and lacquer work are also frequently found in small articles of furniture; and the collection of drawings by native artists attests the high skill in design and execution attained by Indian craftsmen.



