The diaspore bank has been analysed at both shrub sites. In three years of investigation, 58 plant taxa were found in the diaspore bank at the rubble site SA (see Appendix, Table A1). The above-ground vegetation of this site is dominated by tall herbaceous perennial plants such as Solidago gi – gantea and some woody species such as Salix alba and Populus alba with a total of 48 species recorded in the 10×10 m2 plot. The results illustrate the changes in the diaspore banks. However, fluctuations in the occurring taxa also depend partly on the chosen study method. Not all taxa found during seed washing left viable seeds (e. g. Centaurium pulchellum,
Chenopodium rubrum), and applying the seed-emergence method revealed a group of additional taxa (e. g. Echium vulgare, Festuca rubra agg.).
|
S Epigenic species [3 Endogenic species S Anecic species (form (inhabit leaf litter on (inhabit mineral soil permanent vertical soil surface) below surface) burrows) |
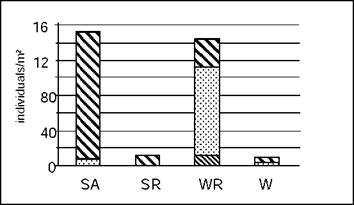
Fig. 3. Abundance and relative proportion of life forms of the lumbricids at the sampled plots. Only shrub and woodland sites are shown, because the pioneer sites were free of lumbricids (for abbreviations see Table 1)
The changes in the diaspore bank diminish further with the progression of ecological succession. Therefore, not only is the number of taxa in the woodland plots low, but the variation in the woodland taxa over the years is extremely low as well.
The other shrub site, SR, is already dominated by pioneer trees (Salix caprea, Betula pendula). Similar to the previous site, birch is the most common species in the diaspore bank, due to a high propagule pressure at both sites. However, at SR, only 25 taxa were found in the diaspore bank (Appendix, Table A2).