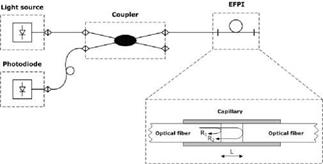
Extrinsic Fabry-Perot interferometric (EFPI) sensors are built from two optical fibres facing each other, but with a small air gap (in the order of micrometers) between them, inside a capillary. The working principle of EFPI sensors is based on multi-reflection Fabry-Perot interference between optical signals reflected from air-glass interface mirrors (Leng & Asundi, 2003). The scheme of the EFPI principle of operation is shown in Fig. 3.
|
Fig. 3. Scheme of system based on extrinsic Fabry-Perot interferometric sensors |
Changes in air gap length (L), which in fact are changes in sensor length, correspond to the variation in the applied mechanical strain. They can be measured by demodulating the interference signal, i. e. by means of coherent or low-coherent techniques (Glisic & Inaudi, 2007).