From Italy the great revival of industrial art travelled to France. Charles VIII., who for two years had held Naples (1494-96), brought amongst other artists from Italy, Bernadino de Brescia and Domenico de Cortona, and Art, which at this time was in a feeble, languishing state in France, began to revive. Francis I. employed an Italian architect to build the Chateau of Fontainebleau, which had hitherto been but an old fashioned hunting box in the middle of the forest, and Leonardo da Vinci and Andrea del Sarto came from Florence to decorate the interior. Guilio Romano, who had assisted Raffaele to paint the loggie of the Vatican, exercised an influence in France, which was transmitted by his pupils for generations. The marriage of Henry II. with Catherine de Medici increased the influence of Italian art, and later that of Marie de Medici with Henri Quatre continued that influence. Diane de
 Poietiers, mistress of Henri II., was the patroness of artists; and Fontainebleau has been well said to "reflect the glories of gay and splendour loving kings from Francois Premier to Henri Quatre."
Poietiers, mistress of Henri II., was the patroness of artists; and Fontainebleau has been well said to "reflect the glories of gay and splendour loving kings from Francois Premier to Henri Quatre."
Besides Fontainebleau, Francis I. built the Chateau of Chambord,7 that of Chenonceaux on the Loire, the Chateau de Madrid, and others, and commenced the Louvre.
Following their King’s example, the more wealthy of his subjects rebuilt or altered their chateaux and hotels, decorated them in the Italian style, and furnished them with the cabinets, chairs, coffers, armoires, tables, and various other articles, designed after the Italian models.
The character of the woodwork naturally accompanied the design of the building. Fireplaces, which until the end of the fifteenth century had been of stone, were now made of oak, richly carved and ornamented with the armorial bearings of the "seigneur." The Frie dieu chair, which Viollet le Due tells us came into use in the fifteenth century, was now made larger and more ornate, in some cases becoming what might almost be termed a small oratory, the back being carved in the form of an altar, and the utmost care lavished on the work. It must be remembered that in France, until the end of the fifteenth century, there were no benches or seats in the churches, and, therefore, prayers were said by the aristocracy in the private chapel of the chateau, and by the middle classes in the chief room of the house.
ORNAMENTAL PAMELUNQ IN ST. VINCENTS CHURCH. ROUEN,
Piituon : Eauly Frekc. m Rus.’lj^sAsce, Trwp. FEMsStputs Lr
|
CHIMNEY PIECE. ht і he CfiJlery of If., ChuLean of Fontaineblcao. Fiiiuio; 1’релсіт RitBfAisSA^CE. Eahlv XVI. Сьятіїиї |
The large high-backed chair of the sixteenth century "ohaire a haut dossier," the arm chair "ohaire a bras," "ohaire tournante" for domestic use, are all of this time, and some illustrations will show the highly finished carved work of Renaissance style which prevailed.
Besides the "ohaire" which was reserved for the "seigneur," there were smaller and more convenient stools, the X form supports of which were also carved.
|
CaKV£o 0,Vh pANtt,, J&ATt’U Ini77- |
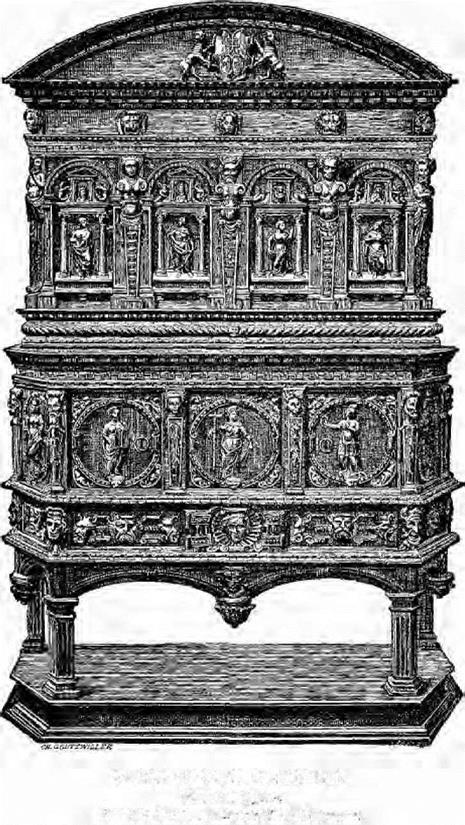
Cabinets were made with an upper and lower part; sometimes the latter was in the form of a stand with caryatides figures like the famous cabinet in the Chateau Fontainebleau, a vignette of which forms the initial letter of this chapter; or were enclosed by doors generally decorated with carving, the upper, part having richly carved panels, which when open disclosed drawers with fronts minutely carved.
M. Edmond Bonnaffe, in his work on the sixteenth century furniture of France, gives no less than 120 illustrations of "tables, ooffres, armoires, dressoirs, sieges, et Banos, manufactured at Orleans, Anjou, Maine, Touraine, Le Berri, Lorraine, Burgundy, Lyons, Provence, Auvergne, Languedoc, and other towns and districts, besides the capital," which excelled in the reputation of her "menuisiers," and in the old documents certain articles of furniture are particularized as "fait a Paris."
He also mentions that Francis I. preferred to employ native workmen, and that the Italians were retained only to furnish the designs and lead the new style; and in giving the names of the most noted French cabinet makers and carvers of this time, he adds that Jacques Lardant and Michel Bourdin received no less than 15,700 livres for a number of "buffets de salles," "tables garnies de leurs treteaux," "chandeliers de bois" and other articles.
|
|
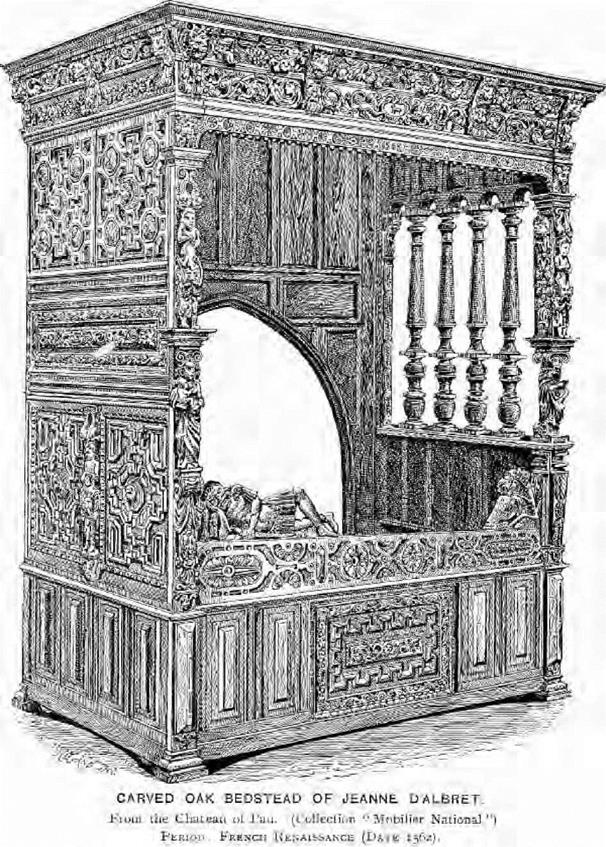
The bedstead, of which there is an illustration, is a good representation of French Renaissance. It formed part of the contents of the Chateau of Pau, and belonged to Jeanne d’Albret, mother of Henri Quatre, who was born at Pau in 1553. The bedstead is of oak, and by time has acquired a rich warm tint, the details of the carving remaining sharp and clear. On the lower cornice moulding, the date 1562 is carved.
This, like other furniture and contents of Palaces in France, forms part of the State or National collection, of which there are excellent illustrations and descriptions in M. Williamson’s "Mobilier National," a valuable contribution to the literature of this subject which should be consulted.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

Another example of four-post bedsteads of French sixteenth century work is that of the one in the Cluny Museum, which is probably some years later than the one at Pau, and in the carved members of the two lower posts, more resembles our English Elizabethan work.
Towards the latter part of Henri IV. the style of decorative art in France became debased and inconsistent. Construction and ornamentation were guided by no principle, but followed the caprice of the individual. Meaningless pilasters, entablatures, and contorted cornices replaced the simpler outline and subordinate enrichment of the time of Henri II., and until the great revival of taste under the "grand monarque," there was in France a period of richly ornamented but ill – designed decorative furniture. An example of this can be seen at South Kensington in the plaster cast of a large chimney-piece from the Chateau of the Seigneur de Villeroy, near Menecy, by Germain Pillon, who died in 1590. In this the failings mentioned above will be readily recognized, and also in another example, namely, that of a carved oak door from the church of St. Maclou, Rouen, by Jean Goujon, in which the work is very fine, but somewhat overdone with enrichment. This cast is in the same collection.
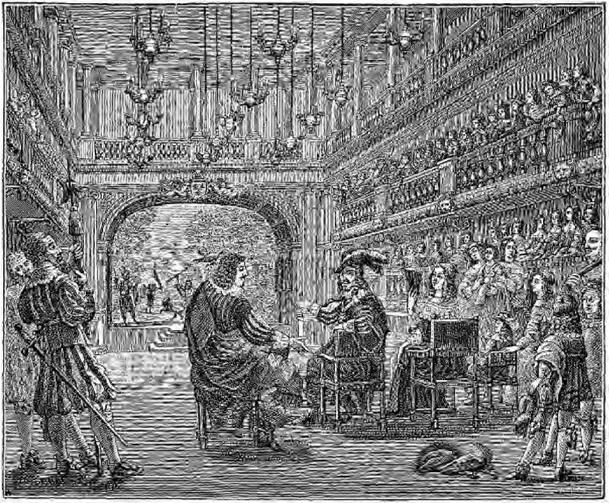
During the ‘Louis Treize’ period chairs became more comfortable than those of an earlier time. The word "chaise" as a diminutive of "chaire" found its way into the French dictionary to denote the less throne-like seat which was in more ordinary use, and, instead of being at this period entirely carved, it was upholstered in velvet, tapestry or needlework; the frame was covered, and only the legs and arms visible and slightly carved. In the illustration here given, the King and his courtiers are seated on chairs such as have been described. Marqueterie was more common; large armoires, clients of drawers and knee-hole writing tables were covered with an inlay of vases of flowers and birds, of a brownish wood, with enrichments of bone and ivory, inserted in a black ground of stained wood, very much like the Dutch inlaid furniture of some years later but with less colour in the various veneers than is found in the Dutch work. Mirrors became larger, the decoration of rooms had ornamental friezes with lower portions of the walls panelled, and the bedrooms of ladies of position began to be more luxuriously furnished.
It is somewhat singular that while Normandy very quickly adopted the new designs in her buildings and her furniture, and Rouen carvers and joiners became famous for their work, the neighbouring province, Brittany, was conservative of her earlier designs. The sturdy Breton has through all changes of style preserved much of the rustic quaintness of his furniture, and when some three or four years ago the writer was stranded in a sailing trip up the Ranee, owing to the shallow state of the river, and had an opportunity of visiting some of the farm houses in the country district a few miles from Dinan, there were still to be seen many examples of this quaint rustic furniture. Curious beds, consisting of shelves for parents and children, form a cupboard in the wall and are shut in during the day by a pair of lattice doors of
Moorish design, with the wheel pattern and spindle perforations. These, with the armoire of similar design, and the "huche" or chest with relief carving, of a design part Moorish, part Byzantine, used as a step to mount to the bed and also as a table, are still the garniture of a good farm house in Brittany.
The earliest date of this quaint furniture is about the middle of the fifteenth century, and has been handed down from father to son by the more well-to-do farmers. The manufacture of armoires, cupboards, tables and doors, is still carried on near St. Malo, where also some of the old specimens may be found.
|
Lvm* КШ. A. N].f М1И Li’iLNiT IN’ ft |IaJL-L= V Г Г їі І;!- -,ІКГ – ■■ і tbAt it hUniittUft d]tUthl ІбЦ. Ї |
|
DECORATION FOR A SALON IN LOUIS XIII. STYLE. |