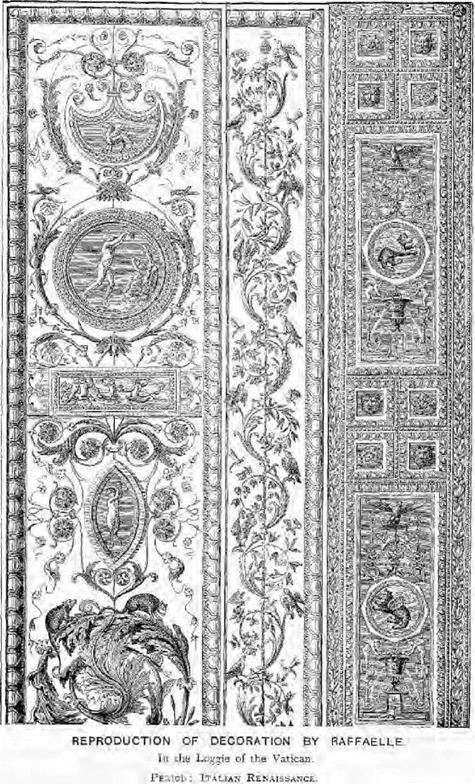
Italy was the birthplace of the Renaissance. Leonardo da Vinci and Raffaele may be said to have guided and led the natural artistic instincts of their countrymen, to discard the Byzantine-Gothic which, as M. Bonnaffe has said, was adopted by the Italians not as a permanent institution, but "faute de mieux" as a passing fashion.
It is difficult to say with any certainty when the first commencement of a new era actually takes place, but there is an incident related in Michael Bryan’s biographical notice of Leonardo da Vinci which gives us an approximate date. Ludovico Sforza, Duke of Milan, had appointed this great master Director of Painting and Architecture in his academy in 1494, and, says Bryan, who obtained his information from contemporary writers, "Leonardo no sooner entered on his office, than he banished all the Gothic principles established by his predecessor, Michelino, and introduced the beautiful simplicity and purity of the Grecian and Roman styles."
A few years after this date, Pope Julius II. commenced to build the present magnificent Church of St. Peter’s, designed by Bramante d’Urbino, kinsman and friend of Raffaele, to whose superintendence Pope Leo X. confided the work on the death of the architect in 1514, Michael Angelo having the charge committed to him some years after Raffaele’s death.
These dates give us a very fair idea of the time at which this important revolution in taste was taking place in Italy, at the end of the fifteenth and the commencement of the following century, and carved woodwork followed the new direction.
|
|
|
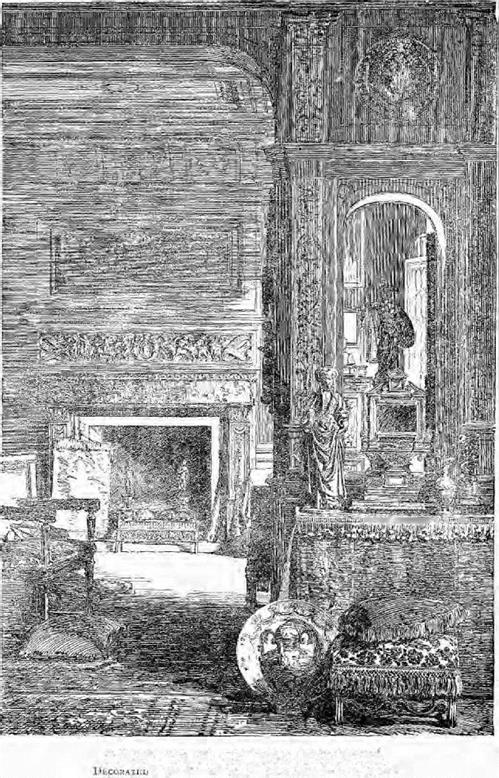
A SIXTEENTH CENTURY ROOM. I(‘t)’r<jduct‘.ii In?1,, till " Miyazina of Art.’ (By [’Агпиззіоіі) |
Leo X. was Pope in 1513. The period of peace which then ensued after war, which for so many decades had disturbed Italy, as France or Germany had in turn striven to acquire her fertile soil, gave the princes and nobles leisure to rebuild and adorn their palaces; and the excavations which were then made brought to light many of the works of art which had remained buried since the time when Rome was mistress of the world. Leo was a member of that remarkable and powerful family the Medicis, the very mention of whom is to suggest the Renaissance, and under his patronage, and with the co-operation of the reigning dukes and princes of the different Italian states, artists were given encouragement and scope for the employment of their talents. Michael Angelo, Titian, Raffaele Sanzio, Andrea del Sarto, Correggio, and many other great artists were raising up monuments of everlasting fame; Palladio was rebuilding the palaces of Italy, which were then the wonder of the world; Benvenuto Cellini and Lorenzo Ghiberti were designing those marvellous chef d’oeuvres in gold, silver, and bronze which are now so rare; and a
|
|
|
|
Оїз ліф тм O-aved Walxul Рп-іиі і і. [fn’ !L..-.I:-t* о[ MTulja*’ Дщг ■■. |
The circumstances of the Italian noble caused him to be very amenable to Art influence. Living chiefly out of doors, his climate rendered him less dependent on the comforts of small rooms, to which more northern people were attached, and his ideas would naturally aspire to pomp and elegance, rather than to home life and utility. Instead of the warm chimney corner and the comfortable seat, he preferred furniture of a more palatial character for the adornment of the lofty and spacious saloons of his palace, and therefore we find the buffet elaborately carved, with a free treatment of the classic antique which marks the time; it was frequently "garnished" with the beautiful majolica of Urbino, of Pesaro, and of Gubbio. The sarcophagus, or oassone, of oak, or more commonly of chesnut or walnut, sometimes painted and gilded, sometimes carved with scrolls and figures; the cabinet designed with architectural outline, and fitted up inside with steps and pillars like a temple; chairs which are wonderful to look upon as guardians of a stately doorway, but uninviting as seats; tables inlaid, gilded, and carved, with slabs of marble or of Florentine Mosaic work, but which from their height are as a rule impossible to use for any domestic purpose; mirrors with richly carved and gilded frames are so many evidences of a style which is palatial rather than domestic, in design as in proportion.
 |
The walls of these handsome saloons or galleries were hung with rich velvet of Genoese manufacture, with stamped and gilt leather, and a composition ornament was also applied to woodwork, and then gilded and painted; this kind of decoration was termed "gesso work."
.
MARRIAGE COFFER,
Carved and Gilt uith Painted Subject.
Italian. XVI. Century.
A rich effect was produced on the carved console tables, chairs, stools and frames intended for gilding, by the method employed by the Venetian and Florentine craftsmen, the gold leaf being laid on a red preparation, and then the chief portions highly burnished. There are in the South Kensington Museum several specimens of such work, and now that time and wear have caused this red groundwork to shew through the faded gold, the harmony of color is very satisfactory.
Other examples of fifteenth century Italian carving, such as the old Cassone fronts, are picked out with gold, the remainder of the work displaying the rich warm color of the walnut or chesnut wood, which were almost invariably employed.
 Of the smaller articles of furniture, the "bellows" and wall brackets of this period deserve mention; the carving of these is very carefully finished, and is frequently very elaborate. The illustration on page 51 is that of a pair of bellows in the South Kensington collection.
Of the smaller articles of furniture, the "bellows" and wall brackets of this period deserve mention; the carving of these is very carefully finished, and is frequently very elaborate. The illustration on page 51 is that of a pair of bellows in the South Kensington collection.
|
|
|
|
The enrichment of woodwork by means of inlaying deserves mention. In the chapter on Ancient Furniture we have seen that ivory was used as an inlaid ornament as early as six centuries before Christ, but its revival and development in Europe probably commenced in Venice about the end of the thirteenth century, in copies of geometrical designs, let into ebony and brown walnut, and into a wood something like rosewood; parts of boxes and chests of these materials are still in existence. Mr. Maskell tells us in his Handbook on "Ivories," that probably owing to the difficulty of procuring ivory in Italy, bone of fine quality was frequently used in its place. All this class of work was known as "Tarsia," "Intarsia," or "Certosina," a word supposed to be derived from the name of the well-known religious community—the Carthusians—on account of the dexterity of those monks at this work.6 It is true that towards the end of the fourteenth century, makers of ornamental furniture began to copy marble mosaic work, by making similar patterns of different woods, and subsequently this branch of industrial art developed from such modest beginnings as the simple pattern of a star, or bandings in different kinds of wood in the panel of a door, to elaborate picture-making, in which landscapes, views of churches, houses and picturesque ruins were copied, figures and animals being also introduced. This work was naturally facilitated and encouraged by increasing commerce between different nations, which rendered available a greater variety of woods. In some of the early Italian "intarsia" the decoration was cut into the surface of the panel piece by piece. As artists became more skilful, veneers were applied and the effect heightened by burning with hot sand the parts requiring shading; and the lines caused by the thickness of the sawcuts were filled in with black wood or stained glue to give definition to the design.
|
Siчп-емти CiJMi’UNv ‘■ Cn ■■ iif.—hi |
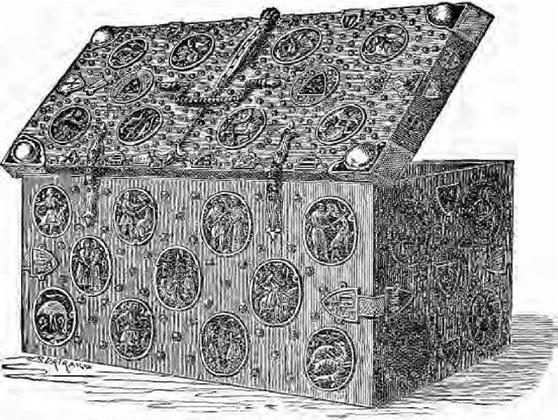
The "mounting" of articles of furniture with metal enrichments doubtless originated in the iron corner pieces and hinge plates, which were used to strengthen the old chests, of which mention has been already made, and as artificers began to render their productions decorative as well as useful, what more natural progress than that the iron corners, bandings, or fastenings, should be of ornamental forged or engraved iron. In the sixteenth century, metal workers reached a point of excellence which has never been surpassed, and those marvels of mountings in steel, iron and brass were produced in Italy and Germany, which are far more important as works of art, than the plain and unpretending productions of the coffer maker, which are their raison d’etre. The woodcut on p. 53 represents a very good example of a "Coffre-fort" in the South Kensington Collection. The decoration is bitten in with acids so as to present the appearance of its being damascened, and the complicated lock, shewn on the inside of the lid, is characteristic of these safeguards for valuable documents at a time when the modern burglar-proof safe had not been thought of.
The illustration on the following page is from an example in the same museum, shewing a different decoration, the oval plaques of figures and coats of arms being of carved ivory let into the surface of the coffer. This is an early specimen, and belongs as much to the last chapter as to the present.
"Pietra-dura" as an ornament was first introduced in Italy during the sixteenth century, and became a fashion. This was an inlay of highly-polished rare marbles, agates, hard pebbles, lapis lazuli, and other stones; ivory was also carved and applied as a bas relief, as well as inlaid in arabesques of the most elaborate designs; tortoiseshell, brass, mother of pearl, and other enrichments were introduced in the decoration of cabinets and of caskets; silver plaques embossed and engraved were pressed into the service as the native princes of Florence, Urbino, Ferrara, and other independent cities vied with Rome, Venice, and Naples in sumptuousness of ornament, and lavishness of expense, until the inevitable period of decline supervened in which exaggeration of ornament and prodigality of decoration gave the eye no repose.
Edmond Bonnaffe, contrasting the latter period of Italian Renaissance with that of sixteenth century French woodwork, has pithily remarked: "Chez cux, I’art du bois consiste a le dissimuler, chez nous a le faire valoir."
In Ruskin’s "Stones of Venice," the author alludes to this over-ornamentation of the latter Renaissance in severe terms. After describing the progress of art in Venice from Byzantine to Gothic, and from Gothic to Renaissance he subdivides the latter period into three classes:—1. Renaissance grafted on Byzantine. 2. Renaissance grafted on Gothic. 3. Renaissance grafted on Renaissance, and this last the veteran art critic calls "double darkness," one of his characteristic terms of condemnation which many of us cannot follow, but the spirit of which we can appreciate.
|
Ili-LtiV-J Cor:FT_’ її WITH MEaiUL[f)Mli nr rVdill’j T jjTT-I C|B(NTUttV, (Sltu/.’i fi. rfrtlfj7*iujp i,!infPNjI.’l |
Speaking generally of the character of ornament, we find that whereas in the furniture of the Middle Ages, the subjects for carving were taken from the lives of the saints or from metrical romance, the Renaissance carvers illustrated scenes from classical mythology, and allegories, such as representations of elements, seasons, months, the cardinal virtues, or the battle scenes and triumphal processions of earlier times.
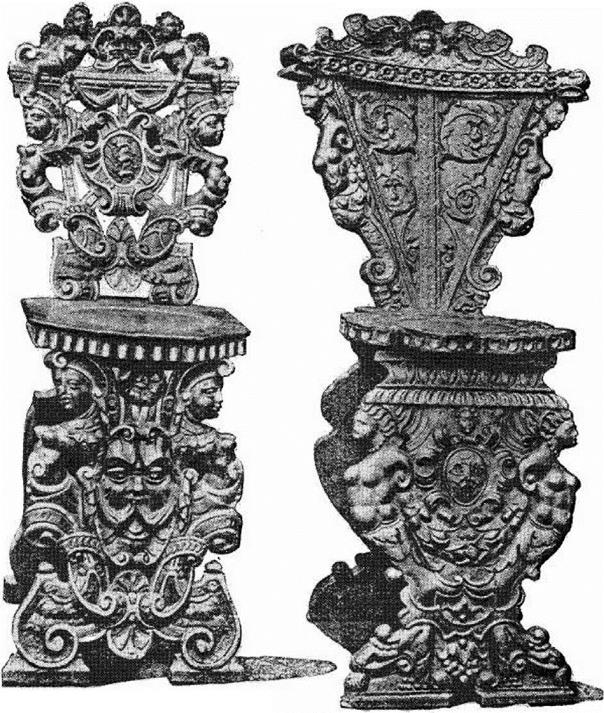
The outlines and general designs of the earlier Renaissance cabinets were apparently suggested by the old Roman triumphal arches and sarcophagi; afterwards these were modified and became varied, elegant and graceful, but latterly as the period of decline was marked, the outlines as shewn in the two chairs on the preceding page became confused and dissipated by over-decoration.
The illustrations given of specimens of furniture of Italian Renaissance render lengthy descriptions unnecessary. So far as it has been possible to do so, a selection has been made to represent the different classes of work, and as there are in the South Kensington Museum numerous examples of cassone fronts, panels, chairs, and cabinets which can be examined, it is easy to form an idea of the decorative woodwork made in Italy during the period we have been considering.

|

|